In today’s digital landscape, organizations heavily rely on cloud computing for their critical data and applications. However, the potential for unforeseen disasters or disruptions necessitates the need for a comprehensive cloud disaster recovery (DR) plan. This article will guide you through the process of creating a cloud disaster recovery plan tailored to the unique requirements of the Microsoft cloud environment. By following the step-by-step approach outlined below, organizations can ensure business continuity, minimize downtime, and protect their valuable assets from natural disasters.
The Importance of a Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
The Consequences of Data Loss and Service Interruptions
Disasters affecting IT systems can have severe repercussions for businesses, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage. Studies show that the majority of system failures are not caused by accidents but rather by human errors, computer viruses, hardware failures, or software glitches. The impact of these incidents can be devastating, with 93% of businesses experiencing some form of damage in the past three years. Implementing a robust cloud disaster recovery plan becomes crucial to mitigate such risks and ensure quick recovery in the face of unforeseen events.
The Purpose of a Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)
A disaster recovery plan is a document that outlines a structured set of steps to recover from an unplanned incident. It is an essential element of a business continuity plan (BCP) and specifically addresses the recovery of IT systems and infrastructure. The primary objective of a DRP is to minimize the adverse consequences of a disaster and enable the organization to resume normal operations and critical operations swiftly.
Designing a Comprehensive Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
Key Considerations and Best Practices
When designing a cloud disaster recovery plan, organizations should consider several key factors and best practices. These include evaluating the specific requirements and priorities of the organization, such as the criticality of data and applications, acceptable downtime levels, and budget constraints. It is crucial to assess the capabilities and limitations of the chosen cloud DR provider, ensuring they align with the organization’s needs. Additionally, considerations regarding data security services such as data encryption, access controls, and compliance requirements should be taken into account to protect sensitive information and meet regulatory standards. By incorporating these considerations and following best practices, organizations can design a robust and effective cloud DR plan.
Differences Between Cloud DR and Traditional DR Methodologies
Understanding the differences between cloud DR and traditional DR methodologies is crucial for organizations transitioning to the cloud. Traditional DR typically involves maintaining a secondary physical data center or backup site for replicating and restoring data and applications. In contrast, cloud DR leverages cloud infrastructure and services, providing higher scalability and flexibility. Cloud DR also offers the advantage of cloud-native features, such as automated workload replication and failover using cloud Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) solutions. By comprehending these differences, organizations can leverage the unique benefits of cloud DR and adapt their own recovery strategies, accordingly.
Leveraging Cloud DRaaS Solutions
Automating workload replication and failover using cloud DRaaS solutions is a critical aspect of cloud DR implementation. DRaaS solutions enable organizations to automate the replication and failover of their workloads, ensuring timely recovery in the event of a disaster. These solutions leverage cloud-native technologies and features to streamline the replication process, eliminate manual intervention, reduce the risk of errors, and improve overall recovery efficiency. Additionally, DRaaS solutions offer flexibility in scaling resources based on demand, providing cost-effectiveness and adaptability to changing business needs.
10 Steps to Create an Effective Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
Identifying Critical Systems and Data The first step in creating a cloud disaster recovery plan is to identify the critical systems and data that require
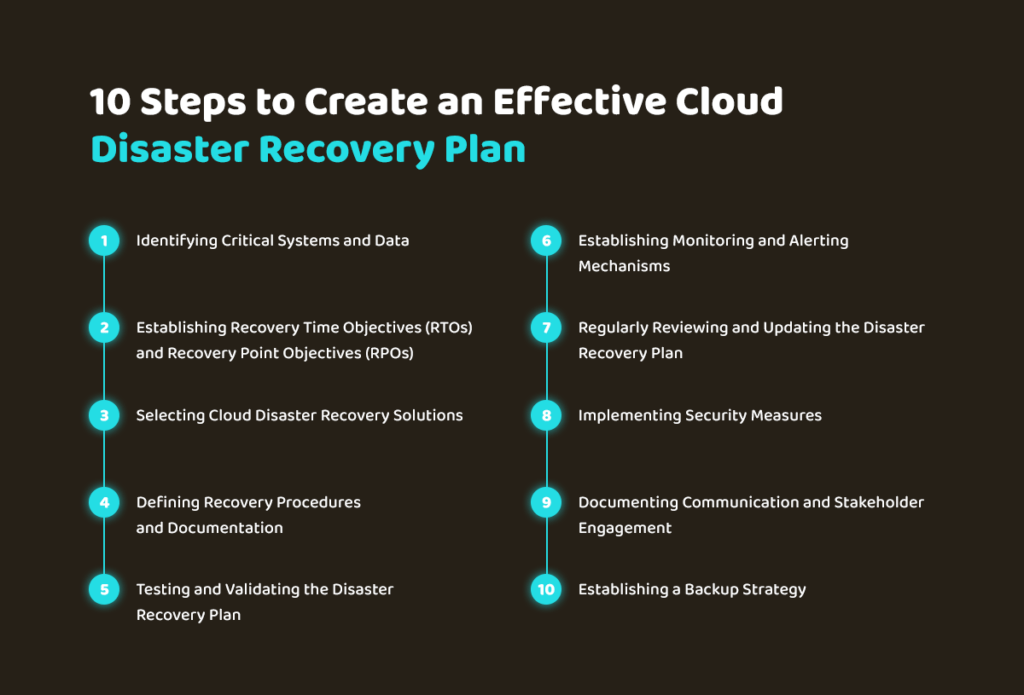
STEP 1: Identifying Critical Systems and Data
The first step in creating a cloud disaster recovery plan is to identify the critical systems and data that require protection. Conduct a thorough assessment of your organization’s IT infrastructure, applications, and data to determine which resources are essential for business operations. Consider factors such as the impact of downtime, data sensitivity, and regulatory compliance requirements. By prioritizing critical systems and sensitive data, you can allocate resources effectively and ensure a focused approach to disaster recovery.
STEP 2: Establishing Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs)
Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) are crucial metrics that define the acceptable downtime and data loss limits in the event of a disaster. RTO represents the maximum allowable time for systems to be down before recovery, while RPO or recovery point objective defines the maximum acceptable data loss in terms of time. Work with key stakeholders to establish realistic RTOs and RPOs based on business requirements, operational dependencies, and the criticality of systems and data. These metrics will guide the design of your cloud disaster recovery strategy and help determine the appropriate technologies and solutions to meet your recovery objectives.
STEP 3: Selecting Cloud Disaster Recovery Solutions
In the Microsoft cloud environment, several solutions and services can facilitate disaster recovery. Microsoft Azure offers robust options such as Azure Site Recovery, Azure Backup, and Azure Storage for replicating and restoring workloads and data. Evaluate these solutions based on their capabilities, compatibility with your existing infrastructure, business impact analysis and alignment with your RTOs and RPOs. Consider factors such as data replication mechanisms, failover and failback processes, network connectivity requirements, and scalability options. Choose the most suitable cloud disaster recovery solutions that meet your organization’s needs and integrate seamlessly with your existing Azure infrastructure.
STEP 4: Defining Recovery Procedures and Documentation
Clearly define the recovery procedures for each critical system and data identified in Step 1. Document the step-by-step instructions to follow during the recovery process, including tasks such as initiating failover, data restoration, system validation, and service resumption. Ensure the documentation at disaster recovery sites is comprehensive, easy to understand, and readily accessible to the designated recovery team. Regularly review and update these recovery procedures to incorporate any changes in your IT infrastructure or applications.
STEP 5: Testing and Validating the Disaster Recovery Plan
Regular testing and validation are vital to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of your cloud disaster recovery plan. Conduct periodic drills and exercises to simulate various disaster scenarios and evaluate the response and recovery processes. Test the failover capabilities, recovery time objective data restoration procedures, and system functionality to verify that the recovery objectives are met. Capture lessons learned from each test and refine the plan accordingly. Testing not only helps identify any gaps or weaknesses in your recovery strategy but also familiarizes the recovery team with their roles and responsibilities during a real disaster event.
STEP 6: Establishing Monitoring and Alerting Mechanisms
Implement robust monitoring and alerting mechanisms to proactively detect potential issues and provide early warning of any deviations from normal system behavior. Leverage the monitoring and logging capabilities offered by Microsoft Azure or third-party tools to track system performance, replication status, and overall health. Configure alerts to notify the relevant teams or stakeholders in case of anomalies or failures. Prompt monitoring and alerting enable swift action and help minimize the impact of a disaster by addressing issues before they escalate.
STEP 7: Regularly Reviewing and Updating the Disaster Recovery Plan
Disaster recovery plans should not be considered static documents. It is essential to review and update the disaster recovery plan template regularly to reflect changes in your IT infrastructure, applications, and business requirements. As your organization evolves, revisit the critical systems and data identified in Step 1, reassess RTOs and RPOs, and ensure that the chosen cloud disaster recovery solutions align with your evolving needs.
Schedule periodic reviews of the disaster recovery plan examples, procedures and documentation outlined in Step 4. Verify that the instructions are up to date and accurately reflect any modifications in your infrastructure or applications. Additionally, conduct regular training sessions for the designated recovery team to keep them informed about any changes and ensure their familiarity with the recovery process.
STEP 8: Implementing Security Measures
Security is a crucial aspect of any disaster recovery plan. When utilizing cloud-based solutions, it is essential to implement robust security measures to protect your data during replication, storage, and recovery. Leverage the security features offered by your chosen cloud provider, such as encryption, access controls, and threat detection. Implement appropriate authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the disaster recovery site or environment. Regularly assess and update your security measures to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
STEP 9: Documenting Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
During a disaster event, effective communication and stakeholder engagement are critical for a successful disaster recovery process. Document a comprehensive communication plan that outlines how you will notify and update key stakeholders, including internal teams, business partners, customers, and regulatory authorities. Define the communication channels, contact information, and escalation procedures to ensure timely and accurate dissemination of information. Regularly review and test your communication plan to validate its effectiveness.
STEP 10 Establishing a Backup Strategy
While a disaster recovery plan focuses on restoring systems and data after a serious disaster occurs, it is equally important to have a robust backup strategy in place. Implement regular backups of critical data and ensure that backups are stored securely in an offsite location, separate from the primary data center. Evaluate the frequency of backups based on data volatility and criticality. Regularly verify the restoration process to verify the integrity and availability of backup data.
Conclusion
Implementing a cloud disaster recovery plan is essential to protect your organization’s critical systems and data from potential disruptions. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a comprehensive and effective it disaster recovery plan that aligns with your business requirements. Remember to identify critical systems and data, establish RTOs and RPOs, select suitable cloud disaster recovery solutions, define recovery procedures, regularly test and validate the plan, establish monitoring mechanisms, review and update the plan periodically, implement security measures, document communication and stakeholder engagement, and establish a backup strategy.
Keep in mind that a cloud disaster recovery plan is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation. By staying proactive and regularly assessing your full disaster recovery planning strategy, you can ensure the resilience and continuity of your business operations even in the face of unexpected events.


