Join us in understanding the importance of multi-cloud architecture and how it revolutionizes business in the cloud era. Jacek Kalwasiński, Cloudica’s Ambassador discovers the benefits, strategies, and challenges of this approach to unlock its full potential.
Why read the article?
Embrace the Cloud Trend: Learn about the accelerated migration to the cloud and why organizations are adopting a “cloud first” strategy.
Unleash Flexibility: Explore how multi-cloud architecture allows business owners to choose the best cloud services from multiple providers, avoiding vendor lock-in and providing the freedom to switch as needed.
Optimize Performance and Costs: Discover how multi-cloud architecture enables cost optimization, high availability, disaster recovery, enhanced security, and better application performance.
Join us on this insightful journey and harness the power of multi-cloud to transform your business.
By Jacek Kalwasiński
Cloudica Ambassador
Understanding the Importance of Multi-Cloud Architecture
In recent years, it is not difficult to notice the trend of migration of organizational systems to the cloud, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and the transition of the operating mode, has significantly accelerated this process. Companies that resisted moving to the cloud were forced to revise their previous assumptions, otherwise, it significantly limited the ability to perform tasks in business. Organizations have realized the benefits of connected systems where information is available anywhere, from any device.
According to Garner’s analysis, by 2025 more than 85% of organizations will adopt a “cloud first” strategy1. By contrast, it estimates that more than 95% of new digital workloads will be deployed on cloud platforms, up from 30% in 2021. It is also obvious that limiting yourself to one supplier is not good practice and creates additional risks in business. An additional benefit of the multicloud strategy is the ability to use best-in-class solutions, which would not be possible with a single provider.
As more organizations move their applications and services to the cloud, multi-cloud architecture has become an increasingly popular strategy. This approach allows companies to leverage multiple cloud providers, platforms, and services simultaneously, providing greater flexibility and agility. In this article, we will discuss the importance of multi-cloud architecture in a cloud computing environment and its benefits.
What is Multi-Cloud?
Multi-cloud is a cloud computing strategy that involves using multiple cloud providers, platforms, and services to meet an organization’s needs. This approach provides flexibility and avoids vendor lock-in, enabling organizations to leverage the unique capabilities of each cloud provider while minimizing the risks of relying on a single provider. Multi-cloud strategies can also help organizations distribute workloads across different cloud providers to optimize performance and reduce costs.
Multi-Cloud Architecture and Management
Multicloud architecture is a project that requires the use of multiple cloud environments to create a seamless, integrated infrastructure. Architecture can include private cloud, multiple public cloud providers, and hybrid cloud environments. Organizations adopting multi-cloud architectures must decide how to transform IT service brokerage, management, architecture, and operations. Choosing an approach for each area of multi-cloud management comes with trade-offs between risk, agility, choice, complexity, cost, functionality, and scalability requirements. These studies will guide you to approach each use case appropriately, considering the strengths of each alternative.
Multi-cloud management involves managing multiple cloud environments and platforms from a single interface. It provides a consolidated view of the entire cloud infrastructure, making it easier to monitor, manage, and optimize resources across different cloud platforms and providers.
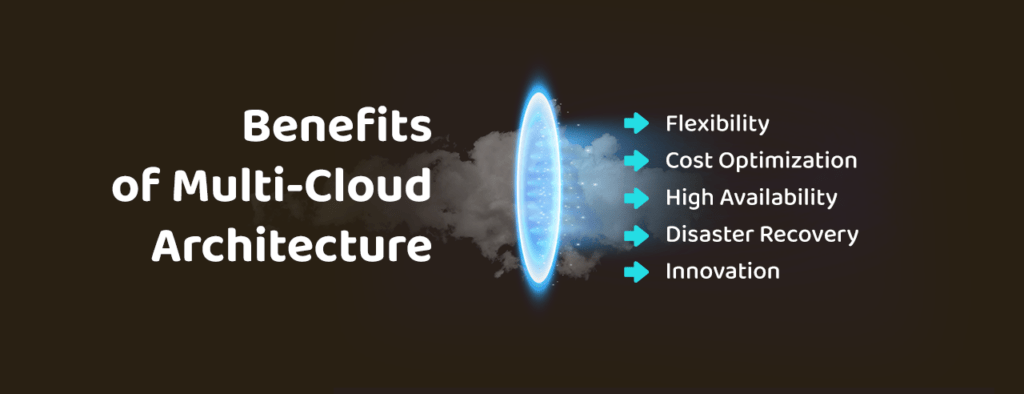
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Architecture
- Flexibility: Multi-cloud architecture allows businesses to select the best cloud services from multiple providers to meet their needs. This approach enables businesses to avoid vendor lock-in and provides the flexibility to switch providers as needed.
- Cost Optimization: Multi-cloud architecture enables businesses to optimize costs by choosing the most cost-effective solutions for different workloads.
- High Availability: Multi-cloud architecture provides high availability by distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, ensuring that services remain available even if one provider experiences downtime.
- Disaster Recovery: Multi-cloud architecture provides disaster recovery capabilities by replicating data across multiple cloud providers, ensuring that data is always available and recoverable in the event of a disaster.
- Innovation: Multi-cloud architecture enables businesses to take advantage of the latest technology and services offered by different cloud providers, driving innovation and competitive advantage.
Multi-Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud are often used interchangeably, but they are different concepts. Hybrid cloud involves using a combination of a public cloud provider and private cloud environments, while multi-cloud involves using multiple cloud providers.
Why Multi-Cloud Strategy is Important?
A multi-cloud strategy is important because it provides greater flexibility, agility, and cost optimization for businesses. It also provides high availability, disaster recovery capabilities, and drives innovation and competitive advantage for cloud vendors. To create a multi-cloud strategy, businesses need to assess their needs, select the best cloud providers for each workload, design a multi-cloud architecture, and implement multi-cloud management tools to monitor and manage the infrastructure.
Disadvantages of Multi-Cloud
Complexity: Managing multiple cloud environments can be complex and require specialized skills.
Security: Multi-cloud architecture can create security risks, particularly if there are data transfers between different cloud providers.
Cost: Multi-cloud architecture can increase costs, particularly if businesses are not careful in selecting the most cost-effective solutions for different workloads.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud
Flexibility: Multi-cloud architecture provides businesses with the flexibility to choose the best cloud services from multiple providers to meet their needs.
Cost Optimization: Multicloud deployment enables businesses to optimize their costs by choosing the most cost-effective cloud services from different providers, based on their budget and performance requirements.
Improved Reliability: By using multiple cloud providers, businesses can distribute their workloads across different clouds, improving the reliability of their applications and reducing the risk of downtime.
Enhanced Security: Multi-cloud architecture can provide enhanced security by distributing workloads across multiple clouds, reducing the risk of data loss or unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Better Performance: Multi-cloud architecture can improve application performance by using the best cloud services for each workload, based on their performance requirements and geographic location.
Vendor Lock-In Avoidance: Multi-cloud architecture can help businesses avoid vendor lock-in, as they are not dependent on a single cloud provider, reducing the risk of being tied to a specific provider’s services.
Security Risks
There are some security risks associated with multi-cloud environments that companies should be aware of. Here are a few:
- Data breaches: The more cloud providers a company uses, the more vulnerable they are to data breaches. This is because each provider has its own security protocols, and it can be challenging to keep track of all of them.
- Misconfigurations: Misconfigurations are a common issue with multi-cloud environments. If a company fails to properly configure one of its cloud services, it could expose sensitive data or create other security vulnerabilities.
- Compliance challenges: Multi-cloud environments can make it difficult to ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. This is because each provider may have different compliance requirements and processes.
- Complexity: Managing multiple cloud providers can be complex, which can increase the likelihood of security issues. For example, it can be challenging to ensure consistent security across all providers.
To mitigate these risks, companies should adopt a multi-layered security strategy that includes encryption, access control, monitoring, and regular security assessments. It’s also important to work closely with each cloud provider to understand their security protocols and compliance requirements. Finally, companies should consider using third-party tools that can help manage security across multiple cloud providers.
Unleashing the Power of Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud architecture offers businesses several advantages over a single cloud deployment. It provides flexibility, cost optimization, improved reliability, enhanced security, better performance, and vendor lock-in avoidance. However, to reap the benefits of multi-cloud, it is important to have a well-defined multi-cloud strategy, effective multi-cloud management, and a clear understanding of the potential challenges and disadvantages of this approach.
Organizations adopting multi-cloud architectures must decide how to transform IT service brokerage, management, architecture, and operations. Choosing an approach for each area of multi-cloud management comes with trade-offs between risk, agility, choice, complexity, cost, functionality, and scalability requirements.
With the right approach, multi-cloud architecture can help achieve business goals, meet performance and budget requirements, and stay competitive in today’s cloud computing landscape.